The U.S. SEC just sent a clear message: decentralized finance (DeFi) isn’t going away — in fact, it reflects the American spirit of innovation, economic freedom, and property rights. In his latest speech, SEC Commissioner Paul Atkins emphasized the value of self-custody and open-access protocols, even hinting at a regulatory framework designed to accommodate DeFi innovation.
For crypto investors, this marks a critical turning point — and puts DeFi-native tokens like Chainlink (LINK) and Uniswap (UNI) back in the spotlight. Both play foundational roles in the DeFi ecosystem, but they serve different purposes and follow different growth paths. As market attention returns to DeFi, understanding how LINK and UNI compare in 2025 is more important than ever.
Key Takeaways
Chainlink is primarily designed as a decentralized oracle network, enabling blockchains to securely interact with off-chain data. It is widely adopted in decentralized finance (DeFi) and enterprise-grade applications for real-time data delivery and interoperability. Uniswap, on the other hand, is a decentralized exchange (DEX) focused on providing a peer-to-peer trading platform using an automated market maker (AMM) model, with a rapidly expanding ecosystem that includes the newly launched Unichain.
Chainlink’s appeal comes from its role as critical infrastructure for Web3, with integrations across major blockchains and enterprises. It powers reliable price feeds, verifiable randomness (VRF), and the Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), which enables seamless multi-chain communication. Meanwhile, Uniswap’s ecosystem thrives on its dominance in decentralized trading and liquidity provision, strengthened by Uniswap v4, scalable Layer 2 deployments, and the launch of Unichain—a dedicated Layer 1 blockchain optimizing DeFi and dApp development.
While Chainlink focuses on ensuring secure and decentralized off-chain data delivery through its robust node network, it has faced criticisms over potential centralization concerns related to its node operators. Uniswap, despite its popularity and technological advancements, has been scrutinized for governance centralization risks, as UNI token whales hold significant influence in voting.
Chainlink is designed as an oracle solution for various use cases, including DeFi protocols, insurance, and gaming, while Uniswap is tailored for trading and liquidity provisioning, positioning it as a leader in the DeFi space. Uniswap’s scalability improvements and the Unichain launch mark a shift towards greater ecosystem independence and innovation.
Both Chainlink (LINK) and Uniswap (UNI) show strong potential in 2024. Chainlink’s adoption will likely be driven by increasing demand for reliable, interoperable data delivery in Web3 applications, while Uniswap’s Unichain and v4 upgrades aim to solidify its position as a leading decentralized exchange. However, Chainlink’s staking rewards and Uniswap’s governance adaptability will be crucial to maintaining their respective ecosystems’ momentum.
Key differences between Chainlink and Uniswap
Key Features (Competitive Advantages)
Chainlink: With its decentralized oracle network, Chainlink connects blockchain-based smart contracts with real-world data, ensuring secure, reliable, and tamper-proof data delivery. Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) further enables seamless multi-chain communication, making it a foundational layer for Web3 infrastructure.
Uniswap: As a leading decentralized exchange (DEX), Uniswap facilitates peer-to-peer trading through an automated market maker (AMM) model. Known for its innovative liquidity pools and scalability, Uniswap’s ecosystem continues to grow with advancements like Uniswap v4 and the launch of Unichain, which optimizes decentralized trading and native dApp development.
Comparison Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Key Features | Decentralized oracle network; secure off-chain data delivery for smart contracts | Decentralized exchange; automated market maker (AMM) model for token swaps |
Long-Term Potential | Infrastructure layer for Web3, DeFi, and cross-chain communication | Leading DEX with scaling solutions, governance, and ecosystem expansion |
Supply | 1 billion tokens (fixed) | 1 billion tokens (fixed) |
Birth Year | 2017 | 2018 |
Consensus Algorithm | Operates on Ethereum; uses decentralized oracle nodes | Operates on Ethereum; AMM model (no mining or staking required) |
Block Generation Time | ~15 seconds (Ethereum-dependent) | ~15 seconds (Ethereum-dependent) |
Performance (1 Years) | +2.1% | -8.9% |
Security | High decentralization and node reliability | Secure protocol but governance subject to centralization risks |
Transaction Speed & Fees | 15 seconds per data delivery; fees depend on network usage ($0.01–$0.05) | ~15 seconds per transaction; fees range from ~$0.05–$5 depending on Layer 1 or Layer 2 usage |
Community Support & Adoption | Developers, node operators, and enterprise partners | Traders, liquidity providers, and DeFi enthusiasts |
Latest Tech Trends | Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP), staking, VRF | Uniswap v4, Unichain (Layer 1), Layer 2 integrations (Optimism, Arbitrum) |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Long-Term Potential
What is Chainlink's Long-term Potential?
Chainlink’s potential as a foundational infrastructure for Web3 and decentralized finance (DeFi) continues to grow as demand for secure, interoperable data solutions rises. Here’s why Chainlink could become a transformative force in the blockchain ecosystem:
Chainlink’s primary strength lies in its ability to provide reliable, decentralized oracle services. LINK, Chainlink’s native cryptocurrency, incentivizes node operators to deliver accurate and secure off-chain data to smart contracts, powering use cases like DeFi price feeds, insurance, gaming, and enterprise blockchain solutions. Chainlink’s Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) is a major advancement, enabling seamless data and token transfers across multiple blockchains. This capability positions Chainlink as critical infrastructure for the multi-chain future of decentralized applications.
Additionally, Chainlink’s staking mechanism enhances network security and reliability by rewarding participants who maintain high-performance nodes. This innovation increases trust in the data delivered to blockchains, encouraging greater adoption by developers and enterprises alike.
But there’s more—Chainlink’s expanding ecosystem is driving innovation in various sectors. Partnerships with leading DeFi protocols like Aave, Synthetix, and Compound underscore its role in powering decentralized finance. Beyond DeFi, Chainlink’s Verifiable Random Function (VRF) supports blockchain gaming and NFTs, while enterprise integrations bring real-world use cases like supply chain monitoring and decentralized insurance to life.
Finally, Chainlink’s commitment to enterprise-grade solutions and regulatory readiness adds another layer of long-term potential. As governments and institutions explore blockchain adoption, Chainlink’s secure and compliant data delivery system makes it an attractive choice for connecting traditional industries to decentralized ecosystems. These developments ensure that Chainlink remains indispensable as Web3 continues to grow.
What is Uniswap's Long-term Potential?
Uniswap’s potential as a cornerstone of decentralized trading and liquidity provision continues to expand as the DeFi ecosystem evolves. Here’s why Uniswap could remain a transformative force in decentralized finance:
Uniswap’s primary strength lies in its role as the largest decentralized exchange (DEX), enabling trustless peer-to-peer token swaps via its automated market maker (AMM) model. UNI, Uniswap’s native token, is central to the governance of the protocol, allowing token holders to vote on major protocol changes and treasury allocations. With the introduction of Uniswap v4 and the launch of Unichain, Uniswap is solidifying its technological leadership in DeFi. Uniswap v4 introduces “hooks,” customizable smart contracts that enable developers to create more flexible and efficient liquidity pools tailored to specific use cases, while Unichain establishes a dedicated Layer 1 blockchain optimized for the Uniswap ecosystem.
Additionally, Uniswap’s integration with Layer 2 solutions such as Optimism and Arbitrum has significantly reduced transaction fees and enhanced scalability, making it accessible to a broader range of users. These improvements address one of the key barriers to adoption—high gas fees on Ethereum—while maintaining a seamless trading experience for users and liquidity providers.
But there’s more—Uniswap’s ecosystem continues to grow, attracting projects across decentralized finance, including lending, staking, and yield farming. Its liquidity pools serve as a foundational layer for numerous DeFi applications, ensuring robust support for tokenized assets and stablecoins. The protocol also plays a critical role in empowering users to create markets for newly launched tokens, fostering innovation in the crypto space.
Finally, Uniswap’s leadership in governance-driven DeFi gives it a unique position in shaping the future of decentralized finance. The launch of Unichain signals a strategic move to reduce reliance on external blockchains and enhance performance, scalability, and user experience for native Uniswap dApps. This positions Uniswap as not just a DEX, but a comprehensive ecosystem for decentralized trading and financial innovation.
As DeFi adoption accelerates globally, Uniswap’s technological advancements, scalability improvements, and governance model ensure that it will continue to thrive as a leader in the decentralized economy.
Aspect | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Core Role | Decentralized Oracle Network for secure off-chain data delivery to smart contracts | Decentralized Exchange (DEX) for token swaps and liquidity provision |
Primary Use Cases | Reliable price feeds, cross-chain interoperability, gaming randomness, and enterprise blockchain | Peer-to-peer trading, liquidity pools, and governance-driven DeFi innovation |
Institutional Appeal | Strong integrations with major DeFi protocols, enterprises, and blockchain projects | Widely adopted in the DeFi ecosystem, with increasing institutional participation through governance |
Security Model | Decentralized node network ensures secure and reliable data delivery | AMM model with robust smart contracts; governance risks mitigated by active community oversight |
Scalability Solutions | Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enables seamless multi-chain operations | Layer 2 integrations (Optimism, Arbitrum) and the launch of Unichain for enhanced scalability |
Long-Term Vision | Foundational Web3 infrastructure for DeFi, gaming, insurance, and cross-chain ecosystems | Comprehensive ecosystem for decentralized trading, scaling, and governance innovation |
Difference between Chainlink and Uniswap in Supply
Chainlink (LINK): LINK has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens. The distribution was pre-mined during its launch, with a significant portion allocated to the Chainlink Foundation for ecosystem development and node operator incentives. This predictable supply structure ensures sufficient liquidity for staking and incentivizing secure oracle operations. The fixed supply enhances LINK’s long-term value proposition but has raised occasional concerns about allocation transparency.
Uniswap (UNI): UNI also has a maximum supply of 1 billion tokens, distributed over a 4-year schedule. A portion of the tokens is allocated to the Uniswap community treasury, team, and investors, ensuring continuous protocol development and community-driven governance initiatives. After the initial token distribution period, no new UNI tokens will be minted, preserving the deflationary nature of the supply.
Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Total Supply Cap | 1 billion | 1 billion |
Annual Issuance | Fixed supply, no new issuance | Initial 4-year distribution, no new issuance after completion |
Key Mechanism | Tokens used to incentivize node operators and ecosystem growth | Governance-driven allocation and treasury management |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Consensus Algorithm
Chainlink: Chainlink does not operate its own blockchain and instead relies on decentralized oracle networks (DONs) built on existing blockchains like Ethereum. These oracles are powered by a network of independent node operators who aggregate off-chain data and deliver it securely to smart contracts. Chainlink’s decentralized structure ensures tamper-proof and reliable data delivery but relies on the security and efficiency of the underlying blockchain it operates on. The introduction of staking mechanisms in Chainlink further enhances trust by incentivizing node operators to provide accurate data.
Uniswap: Uniswap’s AMM (Automated Market Maker) model doesn’t utilize traditional consensus mechanisms like PoW or PoS. Instead, it leverages Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain for security and transaction validation. Uniswap relies on smart contracts to automate token swaps and liquidity provision, ensuring efficient and trustless operations. The simplicity of this approach removes the need for Uniswap to operate its own consensus mechanism, while the scalability and security improvements from Layer 2 integrations like Optimism and Arbitrum enhance its performance.
Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Algorithm | Decentralized Oracle Networks (DONs) | Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) |
Energy Efficiency | Relies on underlying blockchain; highly efficient | Highly efficient with Layer 2 scaling solutions |
Security Model | Independent oracle nodes with staking incentives | Secured by Ethereum’s PoS blockchain and robust smart contracts |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Performance over the past 5 years
Chainlink and Uniswap have both experienced significant growth and volatility. A table of % returns over the last 5 years can illustrate their performance differences:
Metric | Chainlink (Link) | Uniswap (Uni) |
1-Year Return | +2.1% | -8.9% |
5-Year Return | +285.6% | NA |
2025 YTD Return | -30.6% | -43.1% |
Difference Between Chainlink and Uniswap in Security
Chainlink: Secured by its decentralized oracle network (DON), Chainlink relies on independent node operators to aggregate and deliver tamper-proof data to smart contracts. The introduction of staking mechanisms adds an extra layer of security, incentivizing accurate data delivery while penalizing malicious behavior. While highly reliable, Chainlink’s security partially depends on the underlying blockchain (e.g., Ethereum) for transaction validation and network performance.
Uniswap: Secured by Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, Uniswap benefits from the robust security of the Ethereum blockchain. Its smart contracts are the backbone of the automated market maker (AMM) model, ensuring trustless and efficient token swaps. While Uniswap doesn’t face security risks from its consensus mechanism, governance centralization and smart contract vulnerabilities are potential concerns, especially as its ecosystem grows.
Security Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Security Model | Decentralized Oracle Network (DON) with staking incentives | Secured by Ethereum’s PoS blockchain and smart contract audits |
Decentralization | High, reliant on independent node operators | High, reliant on Ethereum validators and robust community |
Energy Consumption | Dependent on underlying blockchain; highly efficient | Efficient with Ethereum PoS and Layer 2 scaling improvements |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Transaction Speed & Fees
Chainlink: Chainlink relies on the transaction speed and scalability of the underlying blockchains it operates on, such as Ethereum, where average block times are ~15 seconds. While the oracle network itself does not directly process transactions, data delivery to smart contracts is efficient, with minimal latency and costs generally tied to blockchain fees. The fees for Chainlink services, like price feeds, are negotiated between node operators and data consumers, ensuring competitive pricing.
Uniswap: Uniswap operates on Ethereum, with transaction speeds dependent on Ethereum’s Proof of Stake (PoS) blockchain (~15 seconds block times). However, integrations with Layer 2 solutions such as Optimism and Arbitrum significantly reduce transaction fees and improve speed, making trading on Uniswap more accessible. Fees for trades on Uniswap include a small percentage of the traded amount (e.g., 0.3% for standard pools), which is distributed to liquidity providers.
Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Transaction Speed | Relies on blockchain (~15–30 TPS on Ethereum) | ~15–30 TPS on Ethereum; faster with Layer 2 solutions (~1,000+ TPS) |
Average Block Time | ~15 seconds (Ethereum-dependent) | ~15 seconds (Ethereum-dependent) |
Fee Structure | Competitive and blockchain-dependent (~$0.01–$0.05) | 0.3% of trade value; lower fees on Layer 2 (~$0.01–$1) |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Earning
Chainlink: LINK’s primary earning opportunities come from price appreciation and staking rewards. Chainlink staking allows LINK holders to lock their tokens and earn rewards while enhancing network security. The reward rates are influenced by demand for oracle services and staking participation.
Uniswap: UNI offers earnings primarily through price appreciation and liquidity provision. Liquidity providers earn a share of the trading fees proportional to their pool contribution. While UNI does not support staking, governance participation gives holders influence over protocol decisions, potentially impacting treasury management and ecosystem growth.
Earning Method | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Price Appreciation | Yes | Yes |
Staking | Yes, via LINK staking | No |
Mining Rewards | No (not mining-based) | No (trading-based rewards for liquidity providers only) |
Chainlink vs. Uniswap: Adoption and Community Support
Chainlink: Chainlink’s adoption centers on its role as critical infrastructure for decentralized applications (dApps), DeFi, and enterprise solutions. Widely integrated across major blockchains and protocols, Chainlink powers price feeds, cross-chain interoperability, and verifiable randomness. Its community includes developers, node operators, and enterprises, with events like SmartCon fostering innovation and engagement. In 2025, Chainlink expanded its adoption across both blockchains and institutions. In mid-May, its Cross‑Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) launched on Solana, while major players like JPMorgan also began leveraging Chainlink’s oracle infrastructure for tokenized asset transactions.
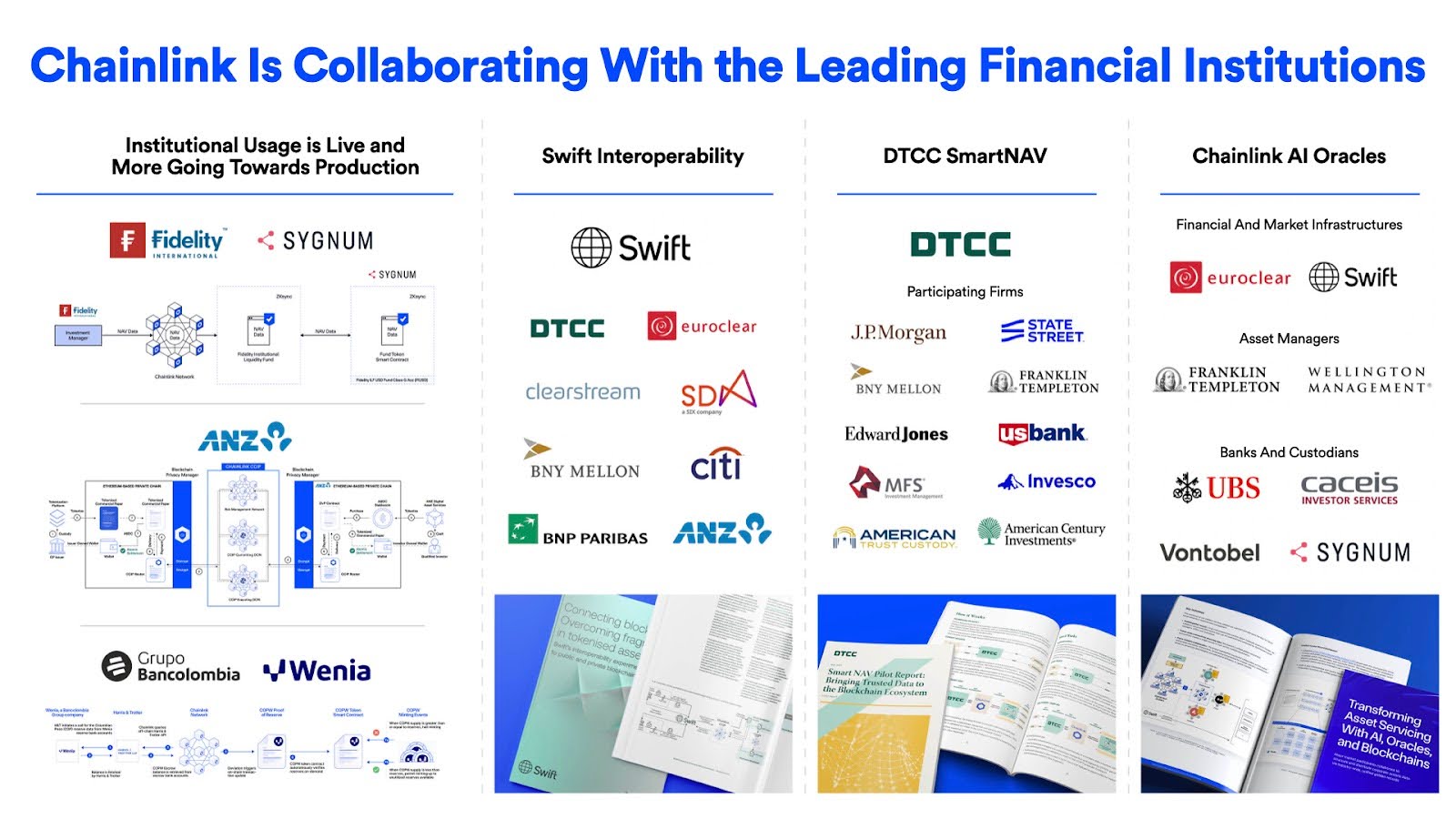
Uniswap: Uniswap is a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem, enabling decentralized trading and liquidity provision. Its user base spans traders, liquidity providers, and developers building on its platform. Events like Uniswap Community Governance and developer-focused initiatives drive participation, while integrations with Layer 2 solutions ensure continued growth and adoption across a broad audience.
Metric | Chainlink | Uniswap |
Use Cases | Decentralized oracle services for dApps, DeFi, gaming, and enterprise | Decentralized trading, liquidity provision, and governance innovation |
Community Size | Large (developers, node operators, enterprises) | Large (traders, liquidity providers, developers) |
Adoption Rate | High in DeFi and enterprise blockchain solutions | High in DeFi and decentralized trading ecosystems |
Chainlink or Uniswap: Which One Is Better?
Wondering which crypto project is the right choice? The answer often depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and preferred use within the blockchain ecosystem. Let’s break it down:
Chainlink: Ideal for those focusing on infrastructure-level solutions, powering Web3 applications with secure, reliable, and decentralized oracle networks.
Uniswap: Best suited for users interested in DeFi trading and liquidity provision, with a robust platform for decentralized financial innovation.
Chainlink: The Backbone of Decentralized Applications
Chainlink’s mission is to provide secure and reliable data for smart contracts, enabling dApps to interact with real-world data. Its decentralized oracle networks deliver services like price feeds, verifiable randomness, and cross-chain interoperability, making it indispensable for DeFi, gaming, and enterprise applications. Chainlink’s partnerships with protocols like Aave and Synthetix demonstrate its utility in powering critical blockchain ecosystems.
Additionally, Chainlink staking incentivizes node operators and token holders to maintain network security and reliability, ensuring its role as foundational Web3 infrastructure. With a growing enterprise focus and integrations across multiple blockchains, Chainlink presents a compelling investment for those prioritizing scalability and utility.
Uniswap: The DeFi Trading Powerhouse
Uniswap revolutionized token trading with its automated market maker (AMM) model, eliminating intermediaries and enabling peer-to-peer transactions. As the largest decentralized exchange (DEX), it continues to dominate DeFi with innovative upgrades like Uniswap v4, which introduces customizable “hooks” for flexible liquidity pools, and Unichain, a dedicated Layer 1 blockchain designed to optimize performance and scalability.
Uniswap also benefits from its community-driven governance, allowing UNI holders to shape the protocol’s future. With integrations on Layer 2 solutions such as Optimism and Arbitrum, Uniswap has reduced fees and increased accessibility, attracting a growing user base and liquidity providers. Its role as a decentralized trading hub ensures its relevance as DeFi adoption accelerates.
So, Which One?
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both Chainlink and Uniswap, you’ll be better equipped to align your investment strategy with your long-term crypto goals.
Choose Chainlink if you value infrastructure-level solutions for powering DeFi and enterprise applications with secure and reliable data.
Choose Uniswap if your focus is on trading and liquidity provision within a robust, decentralized financial ecosystem.
Which one will you choose in this evolving blockchain landscape?


